Analysis by Tim Rowan, Editor Emeritus
The Impact of H.R. 1
Homebound and Overlooked
In early 2025, the Republican-led Congress introduced its proposed budget for FY2026 and beyond, a sweeping legislative effort aimed at curbing federal expenditures and restructuring entitlement programs. Medicaid, one of the largest healthcare safety nets in the United States, faces major revisions under this bill. Central to the proposed changes is the shift toward block grants or per-capita caps on federal funding. The legislation also rolls back incentives enacted into law by the Affordable Care act, including those that supported Medicaid expansion. The reconciliation bill, signed into law on July 4, also eliminates financial support for optional services such as home and community-based services (HCBS). A new set of work requirements in the new law will expand the paperwork burden for beneficiaries.
Risks for Home- and Community-Based Care
The figure below presents a visual from the Commonwealth Fund showing their projection of over $100 billion in cumulative federal Medicaid cuts by 2035. These reductions are expected to disproportionately affect non-mandated programs like HCBS, which are many times more economical than residential care. With diminished federal support, states will face pressure to reallocate limited resources, often at the expense of these optional, yet critical, programs. ¹
For nearly eight million elderly Americans, Medicaid-funded HCBS has helped reduce hospital admissions, extend independence, and relieve stress on long-term care facilities. However, the new budget cuts destabilize these programs. Barbara Merrill, CEO of ANCOR, expressed concern, stating, “When you cut federal Medicaid dollars, even for optional services, states have to make tough decisions about who gets care and when.”² Experts anticipate that approval delays, extended waitlists, and even termination of services could follow as states struggle to maintain existing infrastructure.
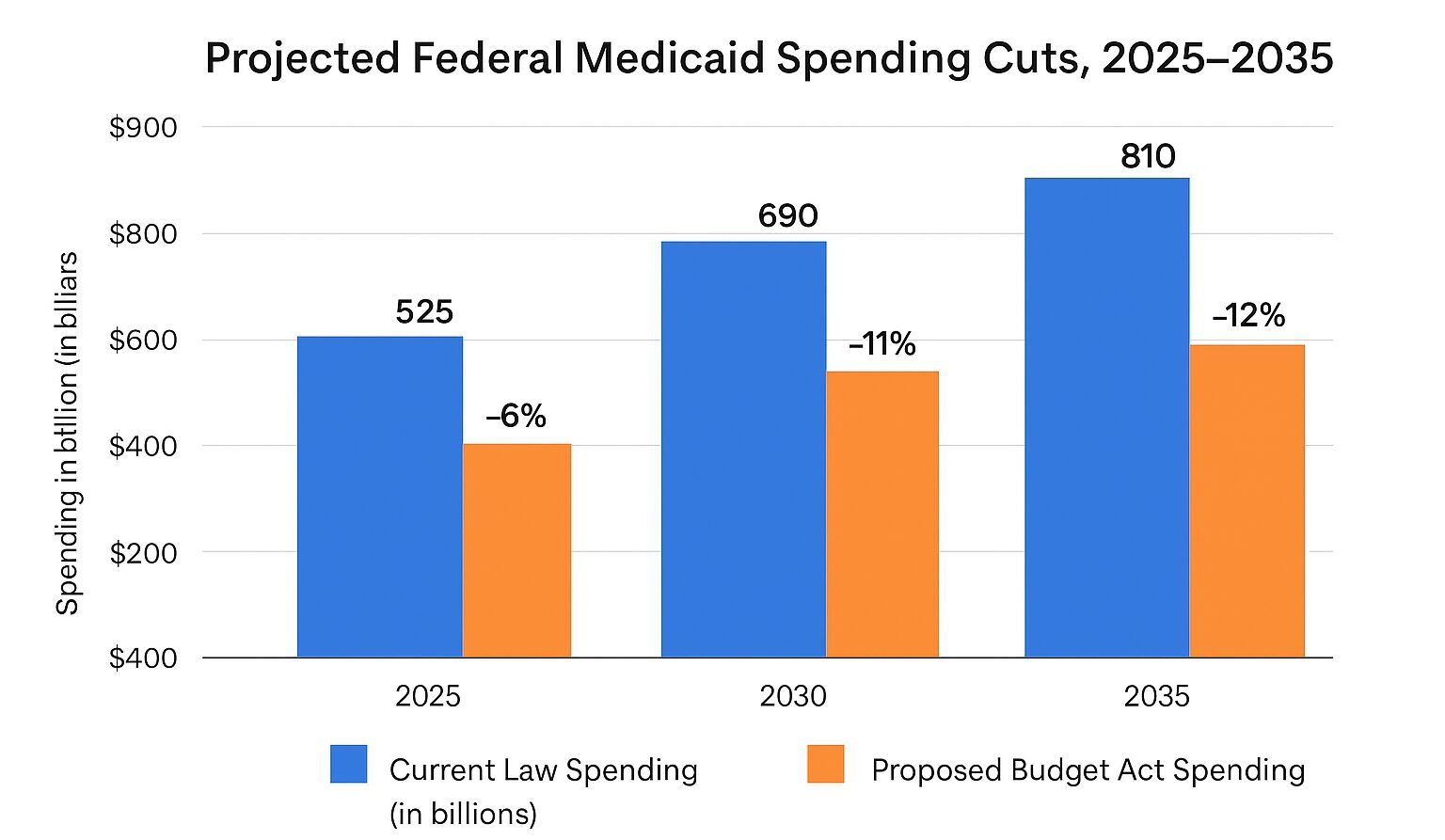
Comparing the 2005 Budget Bill to the Affordable Care Act
Compared to the Affordable Care Act (ACA), the Republican budget bill marks a significant policy reversal. The ACA expanded Medicaid eligibility and incentivized states to develop non-institutional care models. It emphasized preventive care and home-based treatment options, helping shift care away from costly institutional settings. By contrast, the new bill eliminates such incentives and introduces fiscal and operational barriers. According to data from Medicaid.gov and the Kaiser Family Foundation, Medicaid enrollment, which rose steadily during the ACA years, is projected to drop by 10% nationwide once the budget bill is implemented³. This decline reflects both tightening eligibility and retreat from HCBS programs.
Healthcare providers will need to brace for substantial ripple effects. With fewer patients accessing home care, hospitals and emergency departments may see an uptick in acute episodes related to unmanaged chronic conditions. Providers may also encounter staffing shortages and reduced reimbursements, undermining service quality and sustainability. Richard Edwards, policy director at Amivie Home Health, warned, “If states cut home care services, many patients have no other choice but to enter a skilled nursing facility. That’s not just a shift in care—it’s often a worse outcome at a higher cost.” ⁴ These operational challenges could exacerbate pressure on an already strained healthcare workforce.
Scope and Severity of Coming Changes
Today, over eight million seniors rely on Medicaid-funded HCBS, with an average annual cost per recipient of $29,000. Thirty-three states use HCBS waivers to administer these services, yet the average state waitlist already exceeds 3,000 applicants. Institutional care costs remain 57% higher than home care, making HCBS not only more humane but more fiscally prudent. Despite that, projected federal cuts of $100 billion by 2035 threaten to replace HCBS with nursing home care. Meanwhile, a national enrollment drop of 10% would leave millions at risk of losing coverage and care.
Richard Edwards, policy director at Amivie Home Health, explains, “If states cut home care services, many patients have no other choice but to enter a skilled nursing facility. That’s not just a shift in care—it’s often a worse healthcare and social outcome at a higher cost.” ⁴
- 8 million elderly rely on Medicaid HCBS
- $29,000/year average cost per Medicaid home care recipient
- 33 states use HCBS waivers
- Average state waitlist for HCBS exceeds 3,000 applicants
- Institutional care costs 57% more than home care
- Estimated federal Medicaid cuts by 2035: $100 billion
- Projected national enrollment drop: 10%
Implications for Care at Home: Next Steps
Final Thoughts
Ultimately, the new budget, passed with no Democratic votes, may reshape eldercare delivery for years to come. With states facing hard choices, the healthcare community must prepare for transitions that could disrupt care and deepen inequities. Advocacy for vulnerable populations, investment in alternatives, and ongoing engagement in policy reform will be essential to ensure seniors receive the care they deserve in the setting they prefer.
# # #
____________________________________________
¹ Congressional Budget Office, Federal Healthcare Outlook 2025–2035
² Barbara Merrill, ANCOR Policy Brief, March 2025
³ Kaiser Family Foundation, Medicaid Enrollment Tracker, April 2025
⁴ Amivie Health, Testimony to House Budget Committee, June 2025

Tim Rowan is a 30-year home care technology consultant who co-founded and served as Editor and principal writer of this publication for 25 years. He continues to occasionally contribute news and analysis articles under The Rowan Report’s new ownership. He also continues to work part-time as a Home Care recruiting and retention consultant. More information: RowanResources.com
Tim@RowanResources.com
©2025 by The Rowan Report, Peoria, AZ. All rights reserved. This article originally appeared in The Rowan Report. One copy may be printed for personal use: further reproduction by permission only. editor@therowanreport.com



