by Tim Rowan | Jul 26, 2024 | CMS, Editorial, Medicare Advantage, Regulatory
by Tim Rowan, Editor Emeritus
For at least the last five years, every Home Health conference this reporter has attended has featured at least one keynote speaker or expert panelist complaining about sparse and shrinking payments from Medicare Advantage plans. As thousands of seasonal TV ads convince more and more Medicare beneficiaries to enroll in what insurance company executive-turned-whistleblower Wendell Potter called “neither Medicare nor an advantage,” the calls from Home Health executives to turn away MA members, following the lead of many hospitals, have grown louder and more frequent.
Originally designed to extend the lifespan of the Medicare Trust Fund by bringing managed care practices to the federal healthcare program for seniors and disabled, Medicare Advantage has failed to do so. As long ago as 2021, an exposé by Fred Schulte in Kaiser Family Foundation Health News found that MA costs to taxpayers began to explode in 2018 and today equal 119 percent of what traditional Medicare should cost. We looked at more recent studies and found similar reports.
Referencing a study by Richard Kronick, a former federal health policy researcher and a professor at the University of California-San Diego, Schulte said, “his analysis of newly released Medicare Advantage billing data estimates that Medicare overpaid the private health plans by more than $106 billion from 2010 through 2019 because of the way the private plans charge for sicker patients. A third of that overpayment occurred in 2018 and 2019.”
Since Kronick’s 2021 report, more beneficiaries have opted in to Medicare Advantage. So far, just over half have switched from straight Medicare, with or without a supplement, and that number may reach 100 percent if those who profit most from the option have their way.
In recent months, we have investigated and reported on the insurance industry’s practice of
exaggerating MA member health conditions and denying care that traditional Medicare would have covered, collecting from both ends of the CMS trough. We have also mentioned several federal and state lawsuits piling up against insurance companies for both of those practices. One of our sources, The Center for Economic and Policy Research, said this in the Executive Summary of its detailed, September 2023
study:
Profiting at the Expense of Seniors: The Financialization of Home Health Care
“The nonpartisan Medicare Payment Advisory Commission (MedPAC) estimates that upcoding by MA plans that make enrollees appear to be sicker than they are costs CMS 106 percent of what traditional Medicare costs; adding in the quality bonus payments brings it to 108 percent. MA plans also enroll healthier Medicare beneficiaries, increasing their operating surplus by another 11 percent, making the payments to MA plans 19 percent higher than the payments to traditional Medicare.
CMS’s announced goal for traditional Medicare beneficiaries is to move all of them to Accountable Care Organizations, which use the valued-based payment model, or other similar care arrangements, by 2030. CMS’s leading model to accomplish this shift is ACO REACH — a gentler, kinder version of the Trump administration’s backdoor enrollment of traditional Medicare beneficiaries in a capitated payment model.”
The Center for Economic Policy Research
Depending on results in the unpredictable world of politics later this year, CMS may or may not see its shift to value-based ACO models come to fruition. Kaiser News‘ Schulte examined the Heritage Foundation’s “Project 2025,” the conservative think tank’s blueprint for any possible future Republican administration, and found an entire section on the Department of Health and Human Services.
Within its “Mandate for Leadership,” the authors identify Medicare and Medicaid as “the principal drivers of our $31 trillion national debt.” While admitting that Medicare and Medicaid “help many,” the authors assert that the programs “operate as runaway entitlements that stifle medical innovation, encourage fraud, and impede cost containment, in addition to which their fiscal future is in peril.”
Commenting on the Heritage Foundation’s claim, researcher Sonali Kolhatkar, writing for “OtherWords.org,” counters that this opinion is often used to justify ending social programs, but actual CMS data indicates that per person Medicare spending has plateaued for more than a decade and represents one of the greatest reductions to the federal debt. Even with 10,000 to 11,000 Boomers reaching Medicare eligibility every day, total per beneficiary expenditures have stopped climbing, hovering around $12,000 per year since 2010. Before reaching that 2010 plateau, per beneficiary spending had steadily risen from $2,000 at the program’s 1965 inception.
Medicare Advantage for All
Project 2025 proposes making Medicare Advantage the default enrollment option rather than a choice beneficiaries can opt into. With 100 percent of seniors on MA plans, already historic insurance profits will skyrocket further. But will Medicare beneficiaries benefit as well?
The Center for Economic and Policy Research cites multiple lawsuits that have proven eight of the ten largest MA plans routinely add chronic conditions – some non-existent – to patient assessments at enrollment…or later. We reported recently that UnitedHealth Group, operator of the largest MA plan, recently began sending nurses into homes to search for additional health conditions that would raise company payments from the trust fund. The report we quoted included evidence that these home visit upcodes do not lead to any treatments. The Center added that MA’s “heavily restricted networks damage one’s choice of provider along with introducing dangerous delays and denials of necessary care.”
As we have mentioned before, Medicare Advantage is neither Medicare nor an Advantage.
Project 2025 also proposes restrictions on Medicaid eligibility by imposing work requirements. The blueprint sees the program for low-income Americans as a “cumbersome, complicated, and unaffordable burden on nearly every state.” Their plan includes bringing private insurance companies in to “manage” care.
A June, 2024 report by the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities concluded that the ACA’s expansion of Medicaid helped millions of Americans who would otherwise be uninsured, and that its enabling and encouragement of preventive care actually saved money in state budgets. Last month’s report asserted “the people who gained coverage have grown healthier and more financially secure, while long-standing racial inequities in health outcomes, coverage, and access to care have shrunk.”
Project 2025 authors make no mention of a KFF News report from April 2023 that said most Medicaid-eligible people are already working. Nor does it take into account a Government Accountability Office report to Congress October 2020 and again in 2023 that determined that hourly wages in many large companies are low enough to keep even full-time workers eligible for Medicaid and SNAP. Walmart and McDonalds, to name two, land in the top five in almost every state for having Medicaid-eligible workers.
EVEN THE WALL STREET JOURNAL IS CRITICAL
Under the front page Headline “Medicare paid $50 billion to insurers for untreated ills,” a detailed WSJ investigation highlighted a number of findings, including:
- “The questionable diagnoses included some for potentially deadly illnesses, such as AIDS, for which patients received no subsequent care, and for conditions people couldn’t possibly have, the analysis showed. Often, neither the patients nor their doctors had any idea.”
- “Instead of saving taxpayers money, Medicare Advantage has added tens of billions of dollars in costs, researchers and some government officials have said.”
- “Medicare Advantage has cost the government an extra $591 billion over the past 18 years, compared with what Medicare would have cost without the help of the private plans, according to a March report of the Medicare Payment Advisory Commission, or MedPAC, a nonpartisan agency that advises Congress. Adjusted for inflation, that amounts to $4,300 per U.S. tax filer.”
- “The Journal reviewed the Medicare data under an agreement with the federal government. The data doesn’t include patients’ names, but covers details of doctor visits, hospital stays, prescriptions and other care.”
Now it is in the Hands of Voters
Home Health, Hospice, and Home Care owners, management, and workers will be voting in November. Consideration of what four years under a Project 2025-friendly administration will mean to businesses dependent on Medicare and Medicare will weigh heavily on their minds as they enter their polling booths.
Tim Rowan is a 30-year home care technology consultant who co-founded and served as Editor and principal writer of this publication for 25 years. He continues to occasionally contribute news and analysis articles under The Rowan Report’s new ownership. He also continues to work part-time as a Home Care recruiting and retention consultant. More information: RowanResources.com
Tim@RowanResources.com
©2024 by The Rowan Report, Peoria, AZ. All rights reserved. This article originally appeared in Healthcare at Home: The Rowan Report.homecaretechreport.com One copy may be printed for personal use: further reproduction by permission only. editor@homecaretechreport.com
by Tim Rowan | Jul 19, 2024 | Admin, Editorial, Medicare Advantage
by Tim Rowan, Editor Emeritus
UnitedHealth Making Home Health Visits
Payer or Competitor…that is the question. According to a report in the Wall Street Journal, and questioned by the insurance industry’s lobbying arm, AHIP, UnitedHealth Group has increased its revenue from the Medicare Trust Fund by $50 billion by “finding” additional health issues during home visits to its MA customers.
In a July 16 investor call, CEO Andrew Witty said UnitedHealth clinicians made more than 2.5 million home health visits to UnitedHealthcare MA members in 2023. Following these visits to more than 500,000 seniors, UnitedHealth upgraded over 300,000 of them to higher payment levels by uncovering health conditions the individual seniors did not know they had.
The WSJ investigation found that between 2018 and 2021, insurers received $50 billion for diagnoses they added to members’ charts. Many of these diagnoses were “questionable,” according to that investigation.
Though a UnitedHealth spokesperson called the analysis “inaccurate and biased,” former UnitedHealth employees told the Journal home visits are often used to add diagnoses. Clinicians say they use software during visits that offer suggestions as to what illnesses a patient might have.
CEO Witty maintained in the investor call that the practice is good for seniors. “UnitedHealth clinicians discovered more than 3 million gaps in care through home visits in 2023,” he reported, “and 75% of patients receive follow-up care in a clinic within 90 days of a home visit.”
He added that the United home visit program “helps patients live healthier lives and saves taxpayers money,” concluding. “…Medicare Advantage makes programs and results like this possible.”
The Journal concluded with the finding that few of these upgraded seniors are ever seen by a physician for their newly discovered health conditions.
Tim Rowan is a 30-year home care technology consultant who co-founded and served as Editor and principal writer of this publication for 25 years. He continues to occasionally contribute news and analysis articles under The Rowan Report’s new ownership. He also continues to work part-time as a Home Care recruiting and retention consultant. More information: RowanResources.com
Tim@RowanResources.com
©2024 by The Rowan Report, Peoria, AZ. All rights reserved. This article originally appeared in Healthcare at Home: The Rowan Report. One copy may be printed for personal use: further reproduction by permission only. editor@therowanreport.com
by Tim Rowan | Jul 12, 2024 | Admin, Regulatory
by Tim Rowan, Editor Emeritus
Overtime and exemption thresholds impact employers trying to balance cost-effective policies with employee fairness. As such, they keep a close eye on rules they must follow that come down from the U.S. Department of Labor. When those rules change, remaining compliant requires a company HR leader to adapt those policies. One of those times is at hand.
Exemption and Overtime Thresholds for Hourly and Salaried Earners
Effective last week, July 1, the annual salary threshold for overtime exemption increased from $35,568 to $43,888. The DoL’s final rule does not stop there but sets another increase on January 1, 2025, to $58,656 per year or $1,128 per week. Salaries below those thresholds cannot be declared “exempt,” meaning they must be paid overtime rates for hours worked over eight per day and forty per week.
Executive Salaries also Affected
In addition to overtime and exemption thresholds, the new rule increases the highly compensated employee threshold twice as well. On July 1, the annual salary threshold increased from $107,432 to $132,964. That annual threshold will increase again on January 1 to $151,164.
Going forward, the DOL will increase all thresholds every three years starting July 1, 2027, relying on up-to-date wage data.
We learned these DoL rule details from Angelo Spinola, Executive Director and lead home care attorney with Polsinelli, a national law firm.
“Home care providers that have been making adjustments to comply with the July 1 deadline may have heard about a recent case out of Texas blocking the July 1 increases. While the Texas court did use a partial injunction blocking the July 1 increase, it only applies to Texas government employees. It does not affect any private employers.”
He recommended that all home health and home care employers continue to make changes as planned to comply with the July 1 increases. Spinola stated that his statements are for informational purposes only and are not intended to be legal advice. His comments quoted here should not be relied upon or used without consulting a lawyer to consider your specific circumstances, possible changes to applicable laws, rules and regulations and other legal issues.
“There are still challenges pending that could affect the January 1, 2025 increases, however, those decisions are not expected for several months, and it is too soon to predict whether that deadline will be affected. We will continue to monitor these cases and provide any updates that may have an effect on the home care industry.”
Angelo Spinola can be reached via email at onlinesolutions@polsinelli.com.
NAHC Comments on Exemption and Overtime Thresholds
“The long-awaited U.S. Department of Labor rule regulating minimum salaries levels to qualify for exemption to the Fair Labor Standards Act was issued today. We strongly advise the home care community to gain a comprehensive understanding of the rule and institute steps for timely compliance. While the changes may have limited impact on most home care companies, noncompliance comes with serious penalties.” – NAHC President Bill Dombi
Tim Rowan is a 30-year home care technology consultant who co-founded and served as Editor and principal writer of this publication for 25 years. He continues to occasionally contribute news and analysis articles under The Rowan Report’s new ownership. He also continues to work part-time as a Home Care recruiting and retention consultant. More information: RowanResources.com
Tim@RowanResources.com
©2024 by The Rowan Report, Peoria, AZ. All rights reserved. This article originally appeared in Healthcare at Home: The Rowan Report.homecaretechreport.com One copy may be printed for personal use: further reproduction by permission only. editor@homecaretechreport.com
by Tim Rowan | Jun 27, 2024 | CMS, Medicare Advantage
by Tim Rowan, Editor Emeritus
We have been keeping an eye on the Medicare Advantage business as the number of beneficiaries who switch exceeds fifty percent. In past reports, we have described the federal lawsuits that accuse MA insurance companies of illicitly padding revenues while illegally denying treatments that straight Medicare would have covered. (See MedPAC Exposes More Medicare Advantage Crimes – 3/20/24)
Until now, we haven’t gone into detail about those independent brokers with the continuous TV commercials every November. It turns out, they may be even more dishonest than the insurance companies themselves.
Perhaps the most famous of these brokers is the one that put Broadway Joe Namath in our living rooms a hundred times a day. The company started life as Health Insurance Innovations, owned by Chicago-based private equity firm Madison Dearborn Partners. After accusations of fraud, the company folded and re-emerged as Benefytt. When the same accusations returned, the owners shut that company down and came back as Blue Lantern Health.
According to Healthcare Uncovered, the firm filed for a state-level bankruptcy equivalent in Delaware last April, called “assignment for the benefit of creditors.” Blue Lantern’s website is down, as are MedicareCoverageHelpline.com and HealthInsurance.com, their signature assets. Nobody answers the 800 number Namath hocked for years.
The bankruptcy litigation revealed a database of 7 million seniors who had been bombarded by 17 million phone calls. The bankruptcy was apparently precipitated by the Federal Trade Commission, which forced Benefytt to pay $100 million to the people it had scammed by selling sham Obamacare plans, with checks distributed to victims in March. The Securities and Exchange Commission forced Health Insurance Innovations and the company’s co-founder Gavin Southwell to pay a $12 million settlement. Another close associate of the company, Steven Dorfman, was convicted of wire fraud in February.
Tolerance for the firm’s deceptive advertising scheme ended with changes to the Medicare Advantage rule in 2023 that took effect in 2024. Blue Lantern stated after the fines were imposed that the new rule was critical to the company’s downfall,
Previously, former HHS Security Alex Azar characterized the Namath ads as “real savings, real options” in Medicare Advantage, ignoring the studies showing that the MA program costs the Trust Fund not less but $140 billion more than original Medicare.
Healthcare Uncovered concluded with this observation, “Further rules imposed since then by the Biden administration are putting even more pressure on Medicare Advantage lead generators, also called ‘third-party marketing organizations.’ (TPMOs) Beginning October 1 of this year, CMS will require that TPMOs get express consent from individuals before selling contact information to other marketers and brokers — a key loophole that enabled the growth of Blue Lantern and its predecessors.”
Don’t worry about Joe Namath’s retirement income though.
He has already landed a gig hawking hearing aids.
Tim Rowan is a 30-year home care technology consultant who co-founded and served as Editor and principal writer of this publication for 25 years. He continues to occasionally contribute news and analysis articles under The Rowan Report’s new ownership. He also continues to work part-time as a Home Care recruiting and retention consultant. More information: RowanResources.com
Tim@RowanResources.com
©2024 by The Rowan Report, Peoria, AZ. All rights reserved. This article originally appeared in Healthcare at Home: The Rowan Report. One copy may be printed for personal use: further reproduction by permission only. editor@therowanreport.com
by Tim Rowan | Jun 13, 2024 | Clinical, Hospice
by Tim Rowan, Editor Emeritus
“This [virtual dementia] tour opened my eyes to the reality of what a dementia patient lives with every day. It is completely different when you walk in their shoes. I highly recommend this program for caregivers.”
“I can’t tell you how the dementia tour workshop has impacted my daily journey with my husband. He is 64 and suffers from a combination of Lewy Body and Frontal Temporal Dementia. We have been navigating this as a family for 7 years. I thought I understood his struggle, but the virtual tour has opened my eyes completely. It was a very emotional experience for me. You have changed our lives.”
“Thanks to this training, I will be a better caregiver starting today!”
These are a few of the comments from caregivers and family members who were trained by the Hospice of Marion County (HMC) in Ocala, Florida. HMC offers training based on research conducted by P.K. Beville, geriatric specialist and founder of Second Wind Dreams®. Second Wind is an international organization offering services to caregivers. Known as “The Virtual Dementia Tour,” the training is a patented, evidence-based, scientific method of building a greater understanding of dementia for clinicians, caregivers, and family members.

Virtual Dementia Tour
Trained facilitators outfit trainees with patented devices that alter their senses. They then guide participants while they try to complete common everyday tasks and exercises. The Virtual Dementia Tour enables caregivers to experience for themselves the physical and mental challenges those with dementia face. This experience helps to provide better person-centered care.
HMC began The Virtual Dementia Tour in 2020 following an endowment from the widower of an Alzheimer’s patient who had been under MCH care. Named after his late wife, the Nancy Renyhart Dementia Education Program offers trainings through the hospice. The training is not only for hospice patient families and care teams, but to others who request it.
Meet the Team
DJ Ryan, Dementia Education RN, is certified by Second Wind Dreams as a Certified Dementia Practitioner. He has been with HMC since 2015 and provides trainings at the hospice offices and in the community. Chief Medical Officer Mery J. Lossada is dual certified in neurology and psychiatry. She has been with HMC since 2007. She works with local police, EMS providers, the department of Children and Family Services, and mental health providers to coordinate healthcare services to the community, including dementia patients and their families.
In its first three and a half years, the Nancy Renyhart Dementia Education Program has provided dementia education to 9,968 people. This number includes 926 first responders and 482 caregivers who have gone through the Virtual Dementia Tour® in the last two years. It also includes 2,026 healthcare professionals and first responders who have gone through the Tour since the inception of the program in January, 2021. 6,534 people have attended 167 dementia presentations. HMC provides all these services at no charge to the individuals or their employers.
Dr. Lossada told us, “We are a non-profit organization, and we have identified the three most common diagnoses leading to admission to hospice care: cardiological, pulmonary, and dementia. We have a specific program for each one of those disorders, each one intended to improve quality of life for the patient and the caregiver. We have seen that these dementia disorders are causing the most distress. Our training program helps with that.”
Outcomes
Nurse DJ Ryan said the reduction in hospitalizations, emergency department visits, and transfers to residential memory care facilities is impossible to translate into a mere financial advantage. He is more familiar with the impact of the training on individuals and families. “In the case of Lewy Body Dementia, which includes hallucinations, we have seen people believe they were being watched, attacked, or had bad guys coming in through the heating vents. One person called 911 475 times one year. Once we get involved with our part of the task force, we get them the resources that they need and get them connected with support to reduce those 911 calls. And the numbers are astounding.”
Ryan told us he has been receiving calls from all over the country inquiring about participating in or duplicating his training program. This interest comes without having engaged in any promotional efforts outside of the HMC web site. DJ can be reached via the HMC web site, hospiceofmarion.org/dementia.
# # #
Tim Rowan is a 30-year home care technology consultant who co-founded and served as Editor and principal writer of this publication for 25 years. He continues to occasionally contribute news and analysis articles under The Rowan Report’s new ownership. He also continues to work part-time as a Home Care recruiting and retention consultant. More information: RowanResources.com or Tim@RowanResources.com
©2024 by The Rowan Report, Peoria, AZ. All rights reserved. This article originally appeared in Healthcare at Home: The Rowan Report. One copy may be printed for personal use: further reproduction by permission only. editor@homecaretechreport.com
by Tim Rowan | May 22, 2024 | Admin, CMS, Regulatory
by Tim Rowan, Editor Emeritus
For the last time, NAHC President Bill Dombi is spending another Spring on airplanes. It is state association meeting season, and the Bill Dombi Spring Tour has been bringing his regular Capitol Hill update from coast to coast, this time adding the announcement that he will retire at the end of the year.
After 40 years with NAHC, the lengthy standing ovation Californians gave him at the end of his Tuesday speech was well-deserved.
Advocacy and Change
Bill’s core message has not changed, though the details of his ongoing battle to force CMS to take HHAs and Hospices more seriously has its 2024-2025 nuances. “Letting Congress know that you are an important healthcare sector, and clearly the most popular sector, is not NAHC’s job alone. Every one of you has power. Use it. Make your voices heard.”
Meetings with the Senate Finance Committee
To illustrate the point, he related a story about his recent visit to Portland to meet with the Chair of the Senate Finance Committee, Ron Wyland (D-OR).
“Senator Wyden has been one of the major roadblocks to Medicare agencies getting fair payment rates. I went to see him with a group of agency owners and workers to describe the hardships the current and planned pay rate cuts will impose, and to explain the exact problems with the dumb formula CMS is using to calculate those pay rates.
“The Senator said, ‘But MedPAC says you make too much money and rates should be cut. Were they wrong? Or has something changed?’
Reaching Agreement…Almost
“Both, the group and I harmonized. One by one, each agency representative told him about the growing demand of an aging population, the difficulty hiring staff with the salaries our low pay rates allow them to pay, and a full litany of all the problems with Medicare Advantage.
“By the end of our meeting, we hadn’t turned him 180 degrees, but I could see he was beginning to turn.”Later, Dombi added, he met with Senator Debbie Stabenow (D-MI), who is not only a member of the same Finance Committee but the fourth in line in the Senate pecking order. She offered to have a conversation with her colleague, and that turned Senator Wyden the rest of the way toward changing his position 180 degrees.
You Can Make a Difference
“If you think you as an individual owner have no power in Sacramento, Congress, or the White House,” Dombi concluded, “think again.”
See sidebar for the complete list of Finance Committee members. Everyone has power, but if you are a voter in one of their states, you have an even more powerful voice.
The Bill Dombi Spring Tour will continue throughout the year until his retirement. Join Dombi at the 2024 Financial Management Conference & Expo in Las Vegas, July 21-23 and at the 2024 Home Care and Hospice Conference and Expo in Tampa, October 20-22.
Senator Ron Wyland (D-OR)
SENATE FINANCE COMMITTEE MEMBERS
Chair: Ron Wyland (D-OR)
Ranking Member: Mike Crapo (R-ID)
Debbie Stabenow (D-MI)
Chuck Grassley (R-IA)
Maria Cantwell (D-WA)
John Cornyn (R-TX)
Robert Menendez (D-NJ)
John Thune (R-SD)
Thomas Carper (D-DE)D-
Tim Scott (R-SC)
Benjamin Cardin (D-MD)
Bill Cassidy (R-LA)
Sherrod Brown (D-OH)
James Lankford (R-OK)
Michael Bennet (D-CO)
Steve Daines (R-MT)
Bob Casey (D-PA)
Todd Young (R-IN)
Mark Warner (D-VA)
John Barrasso (R-WY)
Sheldon Whitehouse (D-RI)
Ron Johnson (R-WI)
Maggie Hassan (D-NH)
Thom Tillis (R-NC)
Catherine Cortez Masto (D-NV)
Marsha Blackburn (R-TN)
Elizabeth Warren (D-MA)
Tim Rowan is a 30-year home care technology consultant who co-founded and served as Editor and principal writer of this publication for 25 years. He continues to occasionally contribute news and analysis articles under The Rowan Report’s new ownership. He also continues to work part-time as a Home Care recruiting and retention consultant. More information: RowanResources.com
Tim@RowanResources.com
©2024 by The Rowan Report, Peoria, AZ. All rights reserved. This article originally appeared in Healthcare at Home: The Rowan Report.homecaretechreport.com One copy may be printed for personal use: further reproduction by permission only. editor@homecaretechreport.com
by Tim Rowan | May 16, 2024 | Admin, Artificial Intelligence, Clinical, New Tech, Outcomes, Product Review, Vendor Watch
by Tim Rowan, Editor Emeritus
For better or worse, healthcare has begun the inevitable adoption of Artificial Intelligence. Before you consider adopting AI technology, know that there is a wrong way and a right way to use AI in healthcare. In a companion article this week, we describe the criticism insurance companies are getting for deploying AI in healthcare to harm patients. As a balance, here is a review of a product that we find to be using AI in healthcare to help both patients and Home Health Agencies.
The Problem
Home Health referral documents from physicians or hospitals can consist of more than 100 electronically transmitted pages. Some agencies report occasional packets exceeding 1,000 pages, often in a variety of data formats. Some are standard data formats, such as a face sheet, but most are unstructured, consisting of images or narrations, sometimes in paragraphs, sometimes in incomplete sentences. Worse, patient data interoperability can be limited by unstructured data.
More often than not, most of these pages are never read. Thoroughly interpreting that much data is nearly impossible for a human. Consequently, nurses too often approach an admission evaluation visit with an incomplete picture of a patient. The result can be gaps in care or treatment, inaccurate OASIS assessments, incomplete or poorly sequenced diagnosis codes, and improper care plans. These obstacles can impact both patient outcomes and agency revenue.
One Newly Available Solution for the Right Way to use AI in Healthcare
We recently attended a product demonstration and followed it up with updated descriptions to learn details about new product developments. Over the next three months, Select Data, in full disclosure one of our sponsors, will be introducing an AI-powered suite of products that has been designed over many years of development to support clinical, data driven decision-making. One by one, it addresses the problems described above.
The new system, SmartCare, empowers clinicians to harness previously hidden insights while reducing bias and cognitive overload. It enables them to steer their decisions with enhanced precision while maintaining their pivotal role in patient care, eliminating one of the common reasons many Home Health administrators hesitate to invite AI into agency processes. It does, however, make the care team’s job easier and facilitates better decision-making.
- AI can read those 100 to 1,000 page referral documents in minutes, where a human may require days.

- SmartCare uses AI to synthesize relevant medical history to provide a care snapshot highlighting the key diagnosis, focus and considerations for care, and recommended OASIS clinical discipline. It highlights any areas for clarification needed from physician or admitting nurse.
- Clinicians can search and index specific words in unstructured data, such as narratives, to instantly identify any detail of a patient’s condition in an easy-to-read interface. Nurses approach the initial OASIS visit armed with all of a referring clinician’s relevant care findings.
- Recommendations for diagnostic codes strictly follow Medicare PDGM guidelines.
Suite of Tools
1 – RISE stand for Rapid Intake Summary & Evaluation. This component of the suite summarizes all clinical data from referral sources and your EHR. It compiles this data to provide clinically relevant diagnoses, focus of care, and recommendations for skilled disciplines. This is the part of the tool that reads referral documents and supports informed decision-making. The advantages we detected go a bit beyond the technical.
When clinicians, reviewers, coders, and office staff all have access to the same patient information, it would seem that communication among disciplines would improve and that care coordination would be enhanced. It also seems logical that continued experiences of advanced access to previously hard-to-find physician comments would gradually break through the AI fear barrier reported by so many clinicians and other professionals. Select Data will provide us with actual client experiences to verify our assumptions once they have been compiled.
2 – ACE, or Admission Clinical Evaluation is SmartCare’s clinical support summary tool. It deploys AI to understand accepted OASIS assessment criteria. It then uses this knowledge to extract assessment and narrative data from nursing and therapy evaluations. With streamlined, pertinent data at the point of care, the entire care team has the same patient data. Having the same patient data enables more informed decision-making.
ACE links all patient data back to its source assessment. Doubt about the AI’s credibility should gradually diminish, even among the most AI-resistant users. Every analysis and recommendation is explained in clear language so that clinicians are likely to understand the rationale behind them. The goal is to replace every “I’m not going to let a machine tell me what to do” with “I’ll take this information into consideration with my human insights.”
Pricing
We are honoring Select Data’s request to allow them to build personalized price quotes to every prospective client. They will be represented at several state and national conferences this year. Alternatively, interested HHA representatives can contact EVP Ted Schulte at Ted.Schulte@SelectData.com
Tim Rowan is a 30-year home care technology consultant who co-founded and served as Editor and principal writer of this publication for 25 years. He continues to occasionally contribute news and analysis articles under The Rowan Report’s new ownership. He also continues to work part-time as a Home Care recruiting and retention consultant. More information: RowanResources.com
Tim@RowanResources.com
©2024 by The Rowan Report, Peoria, AZ. All rights reserved. This article originally appeared in Healthcare at Home: The Rowan Report.homecaretechreport.com One copy may be printed for personal use: further reproduction by permission only. editor@homecaretechreport.com
by Tim Rowan | May 16, 2024 | Admin, Artificial Intelligence, CMS, Medicare Advantage, Regulatory
by Tim Rowan, Editor Emeritus
Lawsuits are beginning to pile up against insurance companies participating in the Medicare Advantage program. The complaint? The wrong way to use AI in healthcare is with faulty algorithms to approve or deny claims. While AI can be extremely helpful in streamlining administrative tasks — comparing physician notes with Home Health assessments and nursing notes or reading hospital discharge documents — it seems not to be any good at deciding whether to approve or deny care.
The Wrong Way to Use AI in Healthcare Example 1
The Minnesota case, November, 2023, UnitedHealth Group:
-
- An elderly couple’s doctor deemed extended care medically necessary
- UnitedHealth’s MA arm denied that care
- Following their deaths, the couple’s family sued UnitedHealth, alleging:
- Straight Medicare would have approved the extended care
- United uses an AI model developed by NaviHealth called nH Predict to make coverage decisions
- UnitedHealth Group acquired NaviHealth in 2020 and assigned it to its Optum division
- nH Predict is known to be so inaccurate, 90% of its denials are overturned when appealed to the ALJ level
- UnitedHealth Group announced in October, 2023 that its division that deploys nH Predict will longer use the NaviHealth brand name but will refer to that Optum division as “Home & Community Care.”
The family’s complaint stated, “The elderly are prematurely kicked out of care facilities nationwide or forced to deplete family savings to continue receiving necessary medical care, all because [UnitedHealth’s] AI model ‘disagrees’ with their real live doctors’ determinations.”
The Wrong Way to Use AI in Healthcare Example 2
The Class-Action case, December 2023, Humana:
-
- A lawsuit was filed on December 12, 2023 in the U.S, District Court for the Western District of Kentucky
- It was filed by the same Los Angeles law firm that filed the Minnesota case the previous month, Clarkson
- The suit notes that Louisville-based Humana also uses nH Predict from NaviHealth
- The plaintiffs claim, “Humana knows that the nH Predict AI Model predictions are highly inaccurate and are not based on patients’ medical needs but continues to use this system to deny patients’ coverage.”
- The suit says Medicare Advantage patients who are hospitalized for three days usually are eligible to spend as many as 100 days getting follow-up care in a nursing home, but that Humana customers are rarely allowed to stay as long as 14 days.
- A Humana representative said Humana their own employed physicians see AI recommendations but make final coverage decisions.
What Makes This Possible
According to experts we speak with, there are many ways to use data analytics. The insurance companies named in the lawsuits use predictive decision making. This way of analyzing data compares a patient to millions of others and deduces what treatment plan might be suitable for one patient, based on what was effective for most previous patients. Opponents of this method have called it “data supported guessing.”
A superior analysis method experts are coming to understand is prescriptive decision making. This is taking all of the available historical and current data surrounding a patient and making a clinical decision specifically designed to that patient’s age, gender, co-morbidities, doctor recommendations, and treatment records.
Until recently, predictive analysis was the preferred method because of its resource efficiency. Examining the data of every individual patient used to be prohibitively labor-intensive, requiring hours of reading hospital records, physician notes, and claims. Today, however, AI tools are able to do that work in seconds, making prescriptive analytics and customized plans of care possible.
Fix May Be in the Works
In a February 6, 2024 memo to all Medicare Advantage Organizations and Medicare-Medicaid Plans, CMS explained the difference between predictive and prescriptive analytics. The memo said these plans may not make coverage determinations based on aggregated data but must look at each individual:
“For Medicare basic benefits, MA organizations must make medical necessity determinations in accordance with all medical necessity determination requirements, outlined at § 422.101(c)1 ; based on the circumstances of each specific individual, including the patient’s medical history, physician recommendations, and clinical notes; and in line with all fully established Traditional Medicare coverage criteria.”
In response to a request for clarification, the CMS memo laid out its rule in specific language: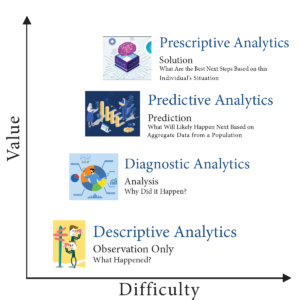
An algorithm or software tool can be used to assist MA plans in making coverage determinations, but it is the responsibility of the MA organization to ensure that the algorithm or artificial intelligence complies with all applicable rules for how coverage determinations by MA organizations are made. For example, compliance is required with all of the rules at § 422.101(c) for making a determination of medical necessity, including that the MA organization base the decision on the individual patient’s circumstances, so an algorithm that determines coverage based on a larger data set instead of the individual patient’s medical history, the physician’s recommendations, or clinical notes would not be compliant with § 422.101(c).
(emphasis added)
“Therefore, the algorithm or software tool should only be used to ensure fidelity with the posted internal coverage criteria which has been made public under § 422.101(b)(6)(ii).”
In further responses to questions in the same memo, CMS made it clear MA plans must make the same coverage decision original Medicare would make. The only allowable exception is that plans may use their own criteria when Medicare Parts A and B coverage criteria “are not fully established.”
Knowledge of this CMS directive may give Home Health agencies one more arrow in their quiver when going to battle with powerful, profit-oriented insurance companies over harmful, illogical AI algorithm decisions.
For information on the right way to use AI in healthcare, see our complimentary article in this week’s issue.
 Tim Rowan is a 30-year home care technology consultant who co-founded and served as Editor and principal writer of this publication for 25 years. He continues to occasionally contribute news and analysis articles under The Rowan Report’s new ownership. He also continues to work part-time as a Home Care recruiting and retention consultant. More information: RowanResources.com
Tim Rowan is a 30-year home care technology consultant who co-founded and served as Editor and principal writer of this publication for 25 years. He continues to occasionally contribute news and analysis articles under The Rowan Report’s new ownership. He also continues to work part-time as a Home Care recruiting and retention consultant. More information: RowanResources.com
Tim@RowanResources.com
©2024 by The Rowan Report, Peoria, AZ. All rights reserved. This article originally appeared in Healthcare at Home: The Rowan Report.homecaretechreport.com One copy may be printed for personal use: further reproduction by permission only. editor@homecaretechreport.com
by Tim Rowan | May 2, 2024 | Admin, Privacy and Security, Regulatory, Telehealth
by Tim Rowan, Editor Emeritus
You know the routine. Everyone does. You log into your bank, airline account, or health insurance web portal, enter the correct password, and are directed to look on your smartphone  for a code to enter to fully authorize your login. The name for this is Multi-Factor Authentication, or MFA. Lack of MFA procedures leaves your company at risk, which UnitedHealth discovered when it was grilled by Congress about the cyberattack on Change Healthcare.
for a code to enter to fully authorize your login. The name for this is Multi-Factor Authentication, or MFA. Lack of MFA procedures leaves your company at risk, which UnitedHealth discovered when it was grilled by Congress about the cyberattack on Change Healthcare.
United Health Grilled by Congress
In his testimony to the House Energy and Commerce Committee Wednesday, UnitedHealth Group CEO Andrew Witty blamed the absence of MFA as the weak link that allowed a ransomware attack to cripple subsidiary Change Healthcare in February. The breach had ripple effects throughout healthcare, given Change’s role as fiscal intermediary for thousands of providers. Healthcare systems on every level were unable to file claims and receive payments.
Asked by the committee why Change Healthcare, which United acquired in late 2022, did not have MFA in place, Witty testified, “Change Healthcare was a relatively older company with older technologies, which we had been working to upgrade since the acquisition. But for some reason, which we continue to investigate, this particular server did not have MFA on it.”
CBS News reported that Change Healthcare processes 15 billion transactions a year. “The scale of the attack,” their report stated, “meant that even patients who weren’t customers of UnitedHealth were potentially affected. Personal information that could cover a ‘substantial portion of people in America’ may have been taken in the attack.” The breach has already cost UnitedHealth Group nearly $900 million, plus the $22 million ransom Witty decided to pay to the hackers.
The Russia-based ransomware gang, ALPHV, or “BlackCat,” claimed responsibility for the attack, bragging that it stole more than six terabytes of data, including “sensitive” medical records. The attack triggered a disruption of payment and claims processing around the country.
We followed up our initial report on the attack with CMS guidance on March 20, 2024 and an update on April 11, 2024, with reports that Change Healthcare was being blackmailed again by another ransomware gang, RansomHub, who claimed to have 4TB of data from Change Healthcare and demanded another ransom payment.
Walmart & Optum, UnitedHealth Trouble Spots?
UnitedHealth Group is also in headline news this week for two other reasons. The company’s Optum division, which owns home care giant CenterWell, formerly Kindred at Home, and which is awaiting government approval for its bid to acquire Amedisys, has quietly been executing a reduction in force. Reports are that the bulk of the layoffs are hitting “Optum Virtual Care,” the name given to naviHealth following its $1 billion acquisition in 2020. Following a surge in demand during the pandemic, the company is apparently abandoning telehealth services.
formerly Kindred at Home, and which is awaiting government approval for its bid to acquire Amedisys, has quietly been executing a reduction in force. Reports are that the bulk of the layoffs are hitting “Optum Virtual Care,” the name given to naviHealth following its $1 billion acquisition in 2020. Following a surge in demand during the pandemic, the company is apparently abandoning telehealth services.
A planned 10-year collaboration between UnitedHealth and Walmart to provide virtual healthcare services ended Tuesday after only one year. On April 30, the retail giant announced that it will close its 51 health centers across five states due to the “challenging reimbursement environment” and rising operating costs, which have resulted in a lack of profitability. Like Optum Virtual Care, the centers were providing virtual services via telehealth.
A sign of the post-pandemic times? Perhaps. We will keep watching.
 Tim Rowan is a 30-year home care technology consultant who co-founded and served as Editor and principal writer of this publication for 25 years. He continues to occasionally contribute news and analysis articles under The Rowan Report’s new ownership. He also continues to work part-time as a Home Care recruiting and retention consultant. More information: RowanResources.com
Tim Rowan is a 30-year home care technology consultant who co-founded and served as Editor and principal writer of this publication for 25 years. He continues to occasionally contribute news and analysis articles under The Rowan Report’s new ownership. He also continues to work part-time as a Home Care recruiting and retention consultant. More information: RowanResources.com
Tim@RowanResources.com
©2024 by The Rowan Report, Peoria, AZ. All rights reserved. This article originally appeared in Healthcare at Home: The Rowan Report.homecaretechreport.com One copy may be printed for personal use: further reproduction by permission only. editor@homecaretechreport.com
by Tim Rowan | Apr 11, 2024 | Clinical, Editorial, Telehealth
by Tim Rowan, Editor Emeritus
In 2020, doctors flooded telehealth companies with requests for help caring for patients reluctant to leave home to come to their appointments. Following suit, many Home Health agencies that had never considered investing in home telehealth before, opened up their wallets to acquire equipment, from simple wearables to high-end, HIPAA-compliant video systems.
In addition to the need to provide care at a safe distance, many HHA leaders knew the added service would attract the attention of hospitals desperate to discharge recovering Covid victims as well as non-Covid patients. Some HHAs established relationships with hospitals they had not had before, given the chance to demonstration Home Health’s unique advantages over extended hospital stays and discharges to institutions such as SNFs that had become virtual death sentences during the height of the pandemic.
All Things Must Pass
 With the introduction and widespread free availability of Covid mRNA vaccines, the death rate graph line began to tilt downward. Then came the discovery that the SARS-CoV-2 and its variants are transmitted through the air and not through unwashed surfaces. People stopped disinfecting their counter tops after unloading groceries. And they started in-person doctor visits again. Patients returned to allowing nurses into their homes.
With the introduction and widespread free availability of Covid mRNA vaccines, the death rate graph line began to tilt downward. Then came the discovery that the SARS-CoV-2 and its variants are transmitted through the air and not through unwashed surfaces. People stopped disinfecting their counter tops after unloading groceries. And they started in-person doctor visits again. Patients returned to allowing nurses into their homes.
In regions where vaccination and booster rates were high, hospitals found themselves with more and more empty beds. They took down tented treatment centers in their parking lots and sent refrigerated trailers back to trucking companies. Desperation referrals to Home Health tapered off, as did the need for virtual visits.
Isaac Newton said every action has an equal and opposite reaction. If that holds true in the healthcare business as it does in physics, the reaction to Covid easing is seen in Remote Patient Monitoring tech companies. According to Fierce Healthcare, the New York Stock Exchange told one RPM company, Amwell, formerly known as “American Well,” to raise its stock price or be delisted. Fierce added detail about the company’s woes:
“Despite decimating its workforce at the end of 2023 to cut expenses, the company still projects a 2024 loss between $160 million and $155 million amid incremental revenue growth. The company’s market cap was a stone’s throw from $6 billion at the height of its valuation, when shares were trading for more than $42 each. Amwell shares were trading at $0.72 as of market close on April 5, giving the company a current market cap of about $208.6 million.
Another market leader fared no better, Fierce Healthcare found. “Telehealth giant Teledoc, which has been in operation for 20 years, has struggled in the stock market and is facing headwinds as the virtual care market has become crowded with digital health players. Shares dropped 22 percent in February as the company missed fourth-quarter revenue estimates and offered a downbeat forecast for the rest of the year.”
Teledoc’s 15-year CEO, Jason Gorevic, resigned last week after the company reported a net loss of $220 million for 2023, following 2022’s historic loss of $13.7 billion, mostly from a write-off related to the plummeting value of its ill-advised Livongo acquisition. According to Fierce Healthcare, Teladoc shelled out $18.5 billion for the digital chronic condition management company, a record in digital health.
Gorevic’s rationale that the telehealth field has become too crowded may not be far off. Last July, Becker’s Hospital Review published an industry survey titled “280+ Telehealth Companies to Know.” The list included a half dozen names we recognized from past Home Health conferences, including Health Recovery Solutions, AMC, Vivify, and FoneMed.
Do Hospital Woes Translate Down to Home Health?
 Making comparisons between telemedicine companies that focus on hospitals and physicians and those who focus on post-acute providers is hampered by the fact that few in our sector are publicly traded and do not share their numbers. UnitedHealth, which acquired Vivify in 2019 and assigned it to its Optum division, does not separately report Vivify revenue.
Making comparisons between telemedicine companies that focus on hospitals and physicians and those who focus on post-acute providers is hampered by the fact that few in our sector are publicly traded and do not share their numbers. UnitedHealth, which acquired Vivify in 2019 and assigned it to its Optum division, does not separately report Vivify revenue.
Health Recovery Solutions, one of the best-known names in post-acute RPM, is privately held by its founding CEO and seven investors. Its most recent influx of $800,000 occurred in January, 2022, making it impossible to determine whether it was motivated by investor confidence or the need for cash as Covid began its decline.
Analysis
This publication has promoted the advantages of remote patient monitoring for its entire 25-year existence. We have covered startups and established tech companies offering every technology from PERS to Zo monitors to automated phone calls, in-home cameras and microphones. We have followed the evolution of two-way communications and vital sign detectors from tabletop devices to tablets and smartphones. We have even tested a few robots. We have seen HHAs experience great success, and we have seen devices collecting dust on shelves.
Throughout, we have maintained that, when selected, implemented, and deployed properly, monitoring patients 24/7 instead of once or twice a week can improve patient outcomes, boost agency reputation, and, more often than not, produce a healthy ROI. The end of the latest pandemic may mean the end of demand for Remote Patient Monitoring systems, but that would be unfortunate.
 Tim Rowan is a 30-year home care technology consultant who co-founded and served as Editor and principal writer of this publication for 25 years. He continues to occasionally contribute news and analysis articles under The Rowan Report’s new ownership. He also continues to work part-time as a Home Care recruiting and retention consultant. More information: RowanResources.com or Tim@RowanResources.com
Tim Rowan is a 30-year home care technology consultant who co-founded and served as Editor and principal writer of this publication for 25 years. He continues to occasionally contribute news and analysis articles under The Rowan Report’s new ownership. He also continues to work part-time as a Home Care recruiting and retention consultant. More information: RowanResources.com or Tim@RowanResources.com
©2024 by The Rowan Report, Peoria, AZ. All rights reserved. This article originally appeared in Healthcare at Home: The Rowan Report. One copy may be printed for personal use: further reproduction by permission only. editor@therowanreport.com













 for a code to enter to fully authorize your login. The name for this is Multi-Factor Authentication, or MFA. Lack of MFA procedures leaves your company at risk, which UnitedHealth discovered when it was grilled by Congress about the cyberattack on Change Healthcare.
for a code to enter to fully authorize your login. The name for this is Multi-Factor Authentication, or MFA. Lack of MFA procedures leaves your company at risk, which UnitedHealth discovered when it was grilled by Congress about the cyberattack on Change Healthcare. formerly Kindred at Home, and which is awaiting government approval for its bid to acquire Amedisys, has quietly been executing a reduction in force. Reports are that the bulk of the layoffs are hitting “Optum Virtual Care,” the name given to naviHealth following its $1 billion acquisition in 2020. Following a surge in demand during the pandemic, the company is apparently abandoning telehealth services.
formerly Kindred at Home, and which is awaiting government approval for its bid to acquire Amedisys, has quietly been executing a reduction in force. Reports are that the bulk of the layoffs are hitting “Optum Virtual Care,” the name given to naviHealth following its $1 billion acquisition in 2020. Following a surge in demand during the pandemic, the company is apparently abandoning telehealth services. With the introduction and widespread free availability of Covid mRNA vaccines, the death rate graph line began to tilt downward. Then came the discovery that the SARS-CoV-2 and its variants are transmitted through the air and not through unwashed surfaces. People stopped disinfecting their counter tops after unloading groceries. And they started in-person doctor visits again. Patients returned to allowing nurses into their homes.
With the introduction and widespread free availability of Covid mRNA vaccines, the death rate graph line began to tilt downward. Then came the discovery that the SARS-CoV-2 and its variants are transmitted through the air and not through unwashed surfaces. People stopped disinfecting their counter tops after unloading groceries. And they started in-person doctor visits again. Patients returned to allowing nurses into their homes. Making comparisons between telemedicine companies that focus on hospitals and physicians and those who focus on post-acute providers is hampered by the fact that few in our sector are publicly traded and do not share their numbers. UnitedHealth, which acquired Vivify in 2019 and assigned it to its Optum division, does not separately report Vivify revenue.
Making comparisons between telemedicine companies that focus on hospitals and physicians and those who focus on post-acute providers is hampered by the fact that few in our sector are publicly traded and do not share their numbers. UnitedHealth, which acquired Vivify in 2019 and assigned it to its Optum division, does not separately report Vivify revenue.

