Government Shutdown
Medicaidby Kristin Rowan, Editor
Government Shutdown Threatens Care at Home
Lawmakers on opposite sides of the aisle failed to come to a budget agreement by the deadline. This causes an immediate cease to all non-essential government functions and many government employees aren’t being paid.
UPDATE: Shutdown, Day 16
–As of October 16, 2025–
What it Means for Care at Home
After 10 attempts, the government is no closer to an agreement than they were on September 30th. The Senate is expected to break at the end of the day, leaving the next opportunity to negotiate until at least Monday.
Telehealth
The biggest impact on care at home during the government shut down is the ability to complete required face-to-face visits using telehealth appointments. Both home health and hospice have employed telehealth for face-to-face encounters since the COVID-era waiver, which has now been extended several times. The most recent extension, which we anticipated Congress to extend in this budget, expired on September 30th.
All face-to-face encounters occurring after October 1, 2025 must be in person.
According to home health expert Melinda A. Gaboury of Healthcare Provider Solutions says it is unlikely an extension would be retroactive even if Congress includes an extension in the finalized budget.
Payments
Conflicting information on Medicare payments leave us unsure of the actual impact. Some reports say there will be no delay while others mention 10-day holds. It is unclear whether this is in addition to the standard 14-day hold. Either way, we are anticipating (and hoping for) minimal payment disruptions.
Surveys
Initial Medicare certification for home health and hospice as well as recertifications will be delayed. If ACHA, CHAP, or another accrediting body is conducting your survey, however, there should be no delay. These accrediting bodies are continuing without interruption. State agency surbveys will be delayed until after the budget is finalized and the shutdown ends.
Look for continued updates from The Rowan Report as the shutdown and negotiations continue.
–As of October 9, 2025–
The Disagreement
Reporters and spokespoeople from both sides of the debate have suggested various reasons for the shutdown. Equally, both sides claim they are not the holdouts. What we do know for sure is that one of the primary points of contention is the continuation of subsidies for Affordable Care Act Marketplace Insurance plans. One group wants an extension written into the current budget while the other says it’s not necessary since the subsidies currently run through the end of the calendar year.
Push to Extend
The lawmakers who are pushing to get the subsidy issue resolved believe that marketplace users are not going to sign up for insurance in November and do it again in January when the subsidies are fixed. Instead, insurance commissioners warn that without the subsidies, many people will opt not to have insurance at all and others will select substandard plans based on affordability. They will be priced out of the plans they want without the subsidies in place.
Priced Out
In 2025, even with the subsidies, the average family was paying $800 per month on health insurance through the marketplace. When the subsidies expire, those same families will see their existing plan rates jump to $3,000 per month. KFF, the nonpartisan health research organization, estimates that most users will have a 114% rate increase.
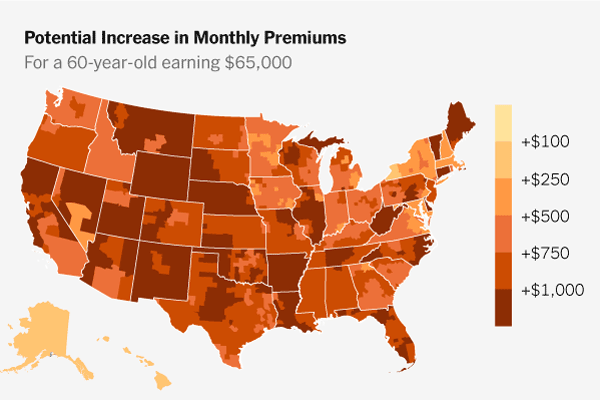
Photo Credit – The New York Times
Counter
According to ND insurance commissioner Jon Godfread, lawmakers who oppose the subsidies are actually opposing the cost of health care and insurance across the board. They insist the subsidies aren’t necessary if healthcare and insurance costs drop instead. Proponents of the subsidies agree, but say that is a longer discussion that will take a lot of time to resolve and the subsidies provide an immediate solution to a bigger problem. They are urging the holdouts to include the subsidies in the budget and tackle the rising cost of healthcare later.
Open Enrollment
The clock is ticking. Open enrollment for 2026 begins November first in every state except Idaho, where open enrollment starts next week. Insurers have already locked in their 2026 premium rates, which will likely cause sticker shock for most marketplace users. Most insurers have prepared subsidy and non-subsidy rates, but without the extension, we will only see the much higher non-subsidy rates. These rates are unlikely to change before enrollment starts and the only hope for marketplace buyers is for Congress to extend the subsidies.

Care at Home Impact
There are several ways in which the shutdown and the loss of the subsidy may impact care at home.
Payment delays are the most pressing risk. Government officials have promised no delay for some essential services like SNAP and WIC. It is likely Medicare and Medicaid payments will be delayed. While those payments will come through eventually, care at home agencies have to operate without payment or hope the
payers will process payments locally while waiting on the government to reopen. The longer the shutdown lasts, the more likely it is that payments will be delayed. The 6th Senate budget vote failed today, sending the shutdown to day 8.
The longer term impact for care at home will come if the subsidies are not renewed. If insurance rates increase by more than 100% on November 1, users will opt for lower priced coverage, which may no longer include care at home benefits. Fewer patients seeking care at home means less money for agencies. Long-term, it also means higher hospital and ER usage and costs, which increases government spending and usually leads to additional care at home cuts to offset the costs.
National Alliance for Care at Home has identifed current and potential implications of the shutdown. Read their analysis here.
This is an ongoing story and we will continue to provide additional information as it happens.
# # #


Kristin Rowan has been working at The Rowan Report since 2008. She is the owner and Editor-in-chief of The Rowan Report, the industry’s most trusted source for care at home news, and speaker on Artificial Intelligence and Lone Worker Safety and state and national conferences.
She also runs Girard Marketing Group, a multi-faceted boutique marketing firm specializing in content creation, social media management, and event marketing. Connect with Kristin directly kristin@girardmarketinggroup.com or www.girardmarketinggroup.com
©2025 by The Rowan Report, Peoria, AZ. All rights reserved. This article originally appeared in The Rowan Report. One copy may be printed for personal use: further reproduction by permission only. editor@therowanreport.com















 Earl L. “Buddy” Carter is an experienced businessman, health care professional and faithful public servant. For over 32 years Buddy owned Carter’s Pharmacy, Inc. where South Georgians trusted him with their most valuable assets: their health, lives and families. While running his business, he learned how to balance a budget and create jobs. He also saw firsthand the devastating impacts of government overregulation which drives his commitment to ensuring that the federal government creates policies to empower business instead of increasing burdens on America’s job creators.
Earl L. “Buddy” Carter is an experienced businessman, health care professional and faithful public servant. For over 32 years Buddy owned Carter’s Pharmacy, Inc. where South Georgians trusted him with their most valuable assets: their health, lives and families. While running his business, he learned how to balance a budget and create jobs. He also saw firsthand the devastating impacts of government overregulation which drives his commitment to ensuring that the federal government creates policies to empower business instead of increasing burdens on America’s job creators. Congressman Ami Bera, M.D. has represented Sacramento County in the U.S. House of Representatives since 2013. The 6th Congressional District is located just east and north of California’s capitol city, Sacramento, and lies entirely within
Congressman Ami Bera, M.D. has represented Sacramento County in the U.S. House of Representatives since 2013. The 6th Congressional District is located just east and north of California’s capitol city, Sacramento, and lies entirely within





