Hospice Fraud Oversight
Adminby Kristin Rowan, Editor
CMS Oversight in Fraud-Ridden States
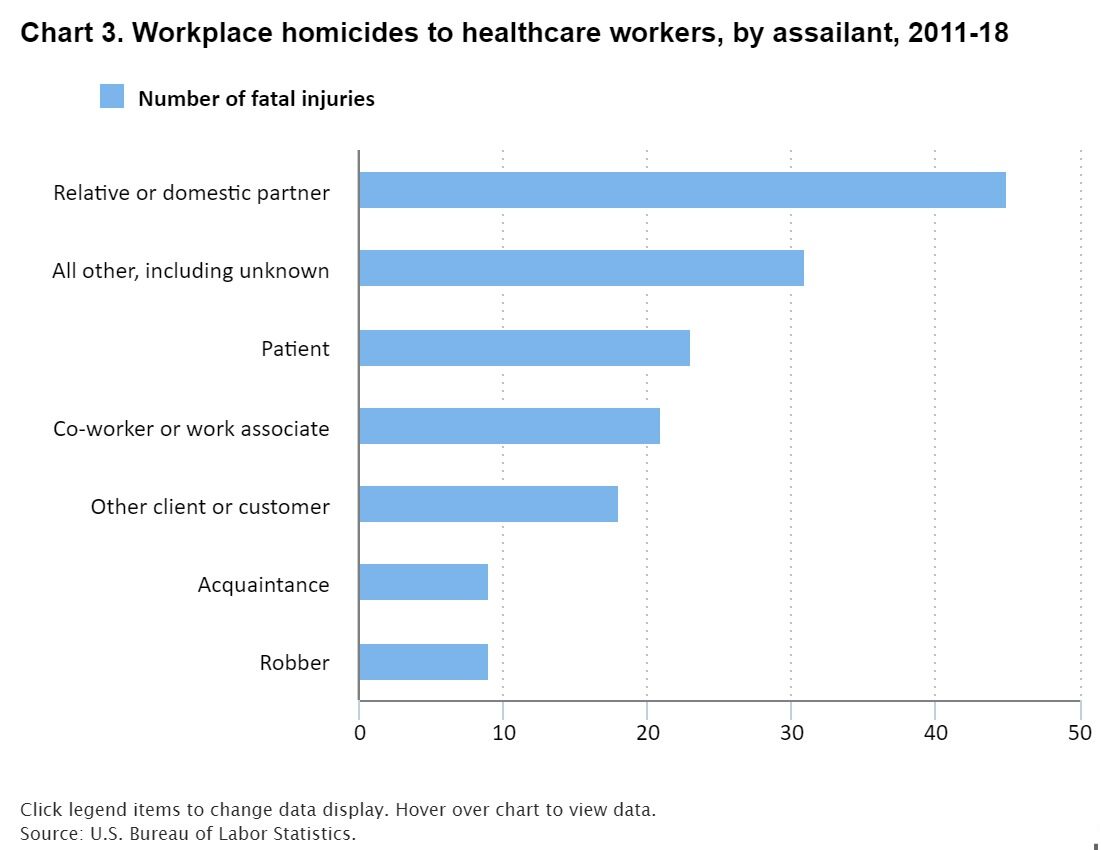
In 2023, The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) cited research suggesting that hospices profit from fraud far too often. CMS has identified cases of hospices certifying benficiaries who are not terminally ill, providing little to no services, and still billing CMS. Four states have had rapid growth in fraudulent hospices: Arizona, California, Nevada, and Texas.
Churn-and-Burn
Some of the registered hospices had non-operational addresses. This information led to an investigation that resulted in evidence of the fraud dubbed “Churn and Burn.” This scheme involves registering a new hospice and billing for services until there is an audit or the agency maxes out on yearly payments. Then, the hospice closes, keeps the money, registers for a new Medicare billing number, and starts all over again.
Program Integrity Strategy
As a result of the findings of this research, CMS put more effort behing the hospice program integrity strategy to find and address fraudulent activity. Part of the strategy was unannounced visits to hospices nationwide. Hospices not active at listed addresses were deactivated and Medicare billing privileges were revoked. Of the more than 7,000 hospices visited, 400 had potential administrative action pending.
Enhanced Oversight
In the four states identified as having higher instances of fraud, CMS implemented a provisional period of enhanced oversight. During the provisional period, CMS conducted a medical review prior to payment for hospices in these states that have identified problems.
Nationwide Pilot Project
In addition to the provisional period for the four identified states, CMS started a pilot project to review hospice claims after a patient’s intitial 90 days of hospice care. This pilot project was not limited to the four states, but was implemented nationwide. CMS launched the program to help inform medical reviews in determining whether hospices are submitting claims for eligible patients.
Regulatory Changes
CMS also proposed some regulatory changes to combat hospice fraud. Some of these regulatory changes were initially suggested by hospice providers. The proposals include:

-
- Prohibiting the transfer of Medicare billing privileges of a new hospice for 36 months
- Clarifying the definition of “Managing Employee” to include the administrator and medical director of a hospice
- Implementing a Special Focus Program to increase oversight on poor-performing hospices that have ongoing health and safety deficiencies
- Adding criminal background checks for owners when they initially enroll for Medicare billing privileges.
Prepayment Review Expanded
CMS has just announced that they will expand the prepayment review process in the four states beginning in September, 2024. Information from CMS is limited and states that prepayment review volume will start low to protect compliant hospices, but will increase if a hospice is found to be non-compliant. Consequences for non-compliance includes delays in payment, extended review, or additional administrative actions.
According to preliminary information we received from a hospice consultant, the expanded program puts all new hospices or hospices with ownership changes into prepayment review even if they have not had identified problems.
We have reached out to both CMS and some of our expert hospice consultants to get more information and will update this story as information becomes available.
# # #


Kristin Rowan has been working at Healthcare at Home: The Rowan Report since 2008. She has a master’s degree in business administration and marketing and runs Girard Marketing Group, a multi-faceted boutique marketing firm specializing in event planning, sales, and marketing strategy. She has recently taken on the role of Editor of The Rowan Report and will add her voice to current Home Care topics as well as marketing tips for home care agencies. Connect with Kristin directly kristin@girardmarketinggroup.com or www.girardmarketinggroup.com
©2024 by The Rowan Report, Peoria, AZ. All rights reserved. This article originally appeared in Healthcare at Home: The Rowan Report. One copy may be printed for personal use: further reproduction by permission only. editor@therowanreport.com



 The financial and health implications of uninformed disenrollment from PACE to conventional MA plans are significant. The needs of PACE beneficiaries, most of whom have multiple complex medical conditions, cognitive or functional impairments – or all three – are not comprehensively addressed by MA plans. The loss of PACE services is harmful and, in some cases, can be life-threatening.
The financial and health implications of uninformed disenrollment from PACE to conventional MA plans are significant. The needs of PACE beneficiaries, most of whom have multiple complex medical conditions, cognitive or functional impairments – or all three – are not comprehensively addressed by MA plans. The loss of PACE services is harmful and, in some cases, can be life-threatening. We share CMS’ stated desire that people have access to accurate and complete information when they make health care choices. We have numerous examples of vulnerable seniors being induced to enroll in MA plans without being fully-informed of what they are giving up when they enroll.
We share CMS’ stated desire that people have access to accurate and complete information when they make health care choices. We have numerous examples of vulnerable seniors being induced to enroll in MA plans without being fully-informed of what they are giving up when they enroll.