Medicaid Enrollees Sent to ICE
by Kristin Rowan, Editor
UPDATE
The Rowan Report originally published this article on August 7, 2025. This update is as of August 15, 2025.
After HHS began providing access to personal data on Mediciad enrollees to the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), 20 states filed to sue the department for violating privacy laws. Shortly thereafter, CMS entered into a new agreement to give DHS daily access to view the same data.
Federal Judge Vince Chhabria of California ordered HHS to stop giving DHS access to personal information. The ruling grants a preliminary injunction, stopping HHS from sharing Medicaid data with ICE in the 20 states that participated in the lawsuit. The injunction will last until 14 days after the two agencies complete and submit a reason for the decision to share information. The reasoning must comply with the Administrative Procedure Act. The injunction can also end if litigation is concluded (a formal hearing and decision).
Chhabria noted that there is no formal law preventing government agencies from sharing information, he cited agency policy as his reasoning for the injunction. ICE has a well-publicized policy against using Medicaid data for immigration enforcement. Judge Chhabria wrote in his ruling:
“Given these policies, and given that the various players in the Medicaid system have relied on them, it was incumbent upon the agencies to carry out a reasoned decisionmaking process before changing them. The record in this case strongly suggests that no such process occurred.”
August 7, 2025
Associated Press Confirms
Enrollee Information Given to ICE
In a surprise announcement on July 17, 2025, investigative reporter Kimberly Kindy and reporter Amanda Seitz filed a report. They uncovered information confirming Medicaid enrollee information given to ICE from CMS. ICE will use this to find “aliens” across the country. The health and personal information disclosed includes home addresses, birth dates, Social Security numbers, and ethnicities.
Department of Homeland Security Responds
DHS Assistant Secretary Tricia McLauglin said, “…CMS and DHS are exploring an intitiative to ensure that illegal aliens are not receiving Medicaid benefits….”
DHS Spokesperson Andrew Nixon said, “With respect to the recent data sharing between CMS and DHS, HHS acted entirely within its legal authority—and in full compliance with all applicable laws….”
Opposing Viewpoints
Senator Adam Schiff (D-CA) said, “The massive transfer of the personal data of millions of Medicaid recipients should alarm every American. This massive violation of our privacy laws must be halted immediately. It will harm families across the nation and only cause more citizens to forego lifesaving access to health care.”
Similarly, CA Governor Gavin Newsom said, “This potential data transfer brought to our attention by the AP is extremely concerning, and if true, potentially unlawful….”
HHS and DHS Sued
State Attorneys General from 20 states, led by California Attorney General Rob Bonta have filed suit. They are suing the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), HHS Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr., and DHS Secretary Kristi Noem.
The Associated Press found a Medicaid internal memo and emails. Subsequently, the AP reported that Medicaid officials tried to stop the data transfer due to legal and ethical concerns. The objection was unsuccessful. CMS had 54 minutes to comply with an order coming from two advisors within Secretary Kennedy Jr’s camp.
Disclosure Focuses on Violation of Laws
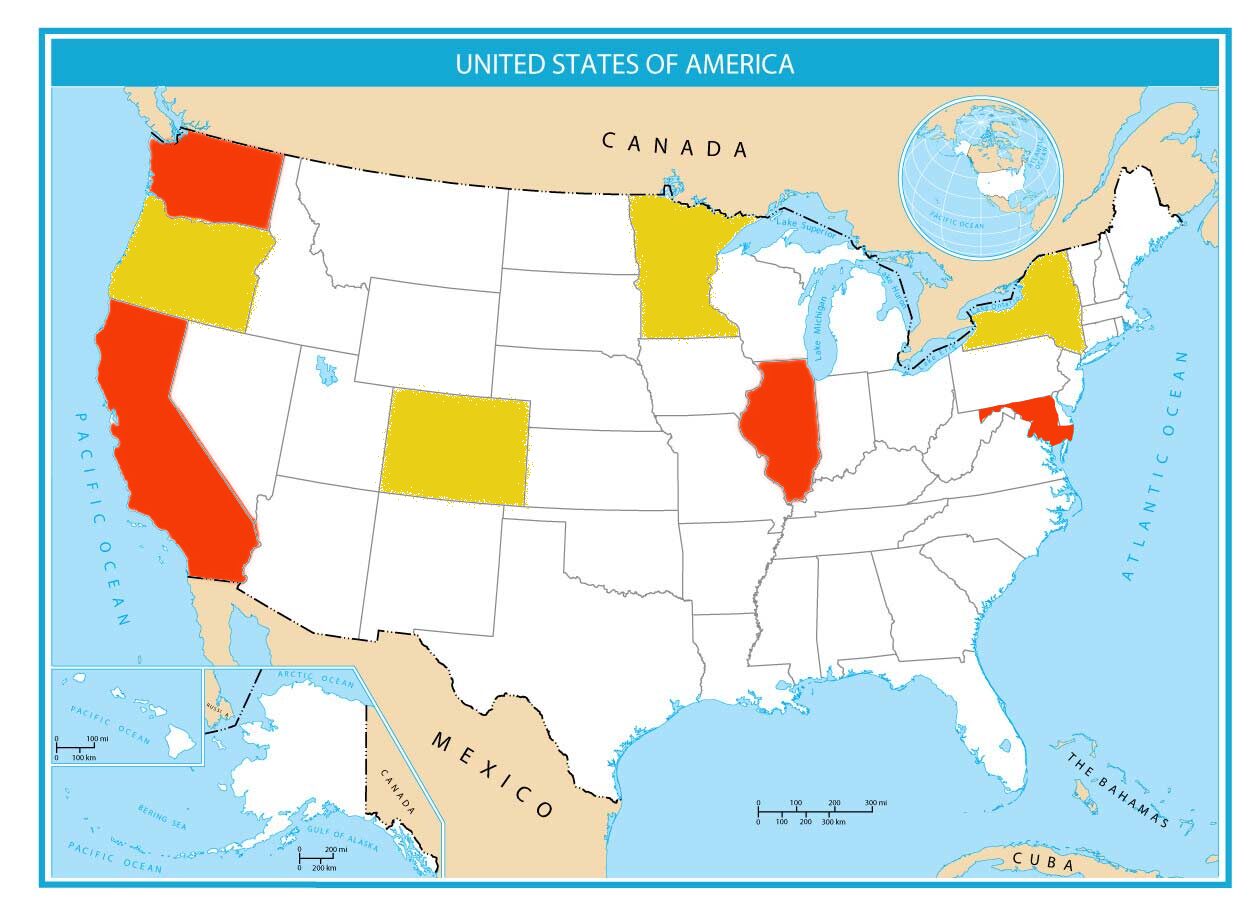
Current laws provide that states can create their own health plans, eligibility standards, and coverage, as long as the plan follows federal criteria. Medicaid laws also provide for emergency coverage for non-citizens. Seven states and D.C. started programs that offer full Medicaid coverage to non-citizens.
Four of the seven states, New York, Oregon, Minnesota, and Colorado, never submitted identifiable information about Medicaid recipients to CMS. The data shared with ICE came from the remaining three states; California, Illinois, & Washington State; and Washington D.C.
The Allegation
The lawsuit was filed in the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California. It alleges that the federal government is allowing the personal data of Medicaid recipients to be used for purposes unrelated to the Medicaid program.
Further, the coalition of states alleges that the disclosures violate several federal data privacy laws. These include Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), Federal Information Security Modernization Act (FISMA), and the Privacy Act.
Additionally, the Attorneys General state that the disclosures are contrary to the Social Security Act and a violation of the Spending Clause.
The lawsuit calls upon the court to bar CMS from sending additional PII to DHS and to bar DHS from using any of the information it has already received.
“In the seven decades since Congress enacted the Medicaid Act to provide medical assistance to vulnerable populations, federal law, policy, and practice has been clear: the personal healthcare data collected about beneficiaries of the program is confidential, to be shared only in certain narrow circumstances that benefit public health and the integrity of the Medicaid program itself.”
Final Thoughts
This lawsuit is the latest of many against the current administration. The Rowan Report will continue to update this and other stories impacting care at home as the lawsuits continue.
# # #


Kristin Rowan has been working at The Rowan Report since 2008. She is the owner and Editor-in-chief of The Rowan Report, the industry’s most trusted source for care at home news, and speaker on Artificial Intelligence and Lone Worker Safety and state and national conferences.
She also runs Girard Marketing Group, a multi-faceted boutique marketing firm specializing in content creation, social media management, and event marketing. Connect with Kristin directly kristin@girardmarketinggroup.com or www.girardmarketinggroup.com
©2025 by The Rowan Report, Peoria, AZ. All rights reserved. This article originally appeared in The Rowan Report. One copy may be printed for personal use: further reproduction by permission only. editor@therowanreport.com